C++ Primer
字典

Part I The Basics
2.1.1

2.1:
C++语言规定一个int至少和一个short一样大,一个long至少和一个int一样大,一个long long至少和一个long一样大。每个的最小尺寸分别为:short,16位;int,16位;long,32位;long long,64位。
除去布尔型和扩展的字符型外,其他整形可以划分为带符号的和无符号的两种。带符号类型可以表示正数、负数或0,无符号类型则仅能表示大于等于0的值。
float最小尺寸为6位有效值,double最小尺寸为10位有效值。
2.2:
都选用double,利率4.5%=0.045,本金和付款金额都是以元为单位,钱的最小金额是分,需要精确到小数点后两位,所以都选用double
2.1.2

2.3:
32、2^32 - 32
32、-32、0、0
2.4:

2.1.3
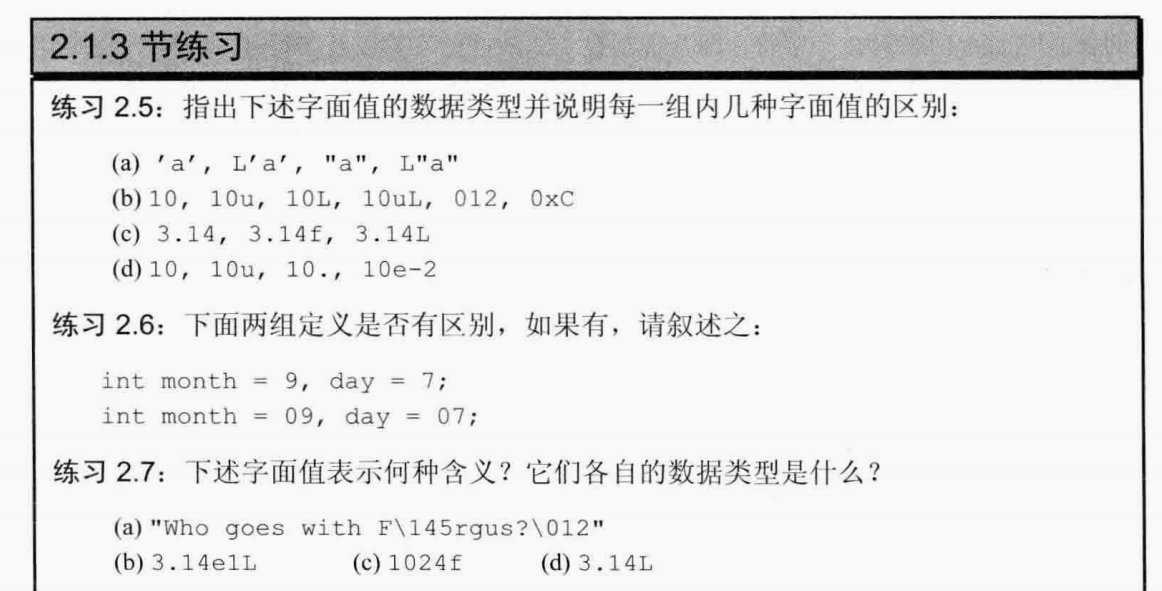
2.5:
(a)字符型,宽字符型,字符串型,宽字符串
(b)整型,无符号整型,长整型,无符号长整型,八进制整型,十六进制整型
(c)浮点型,单精度浮点型,扩展精度浮点型
(d)整型,无符号整型,浮点型,浮点型
2.6:
答:有区别,区别在于上面那行代码定义的month和day为十进制整型数字,而下面的为八进制数,并且int month = 09这句会报错!!!
2.7:
(a)“Who goes with Fergus?” ,string
(b)31.4,long double
(c)3.14,long double
2.2.1
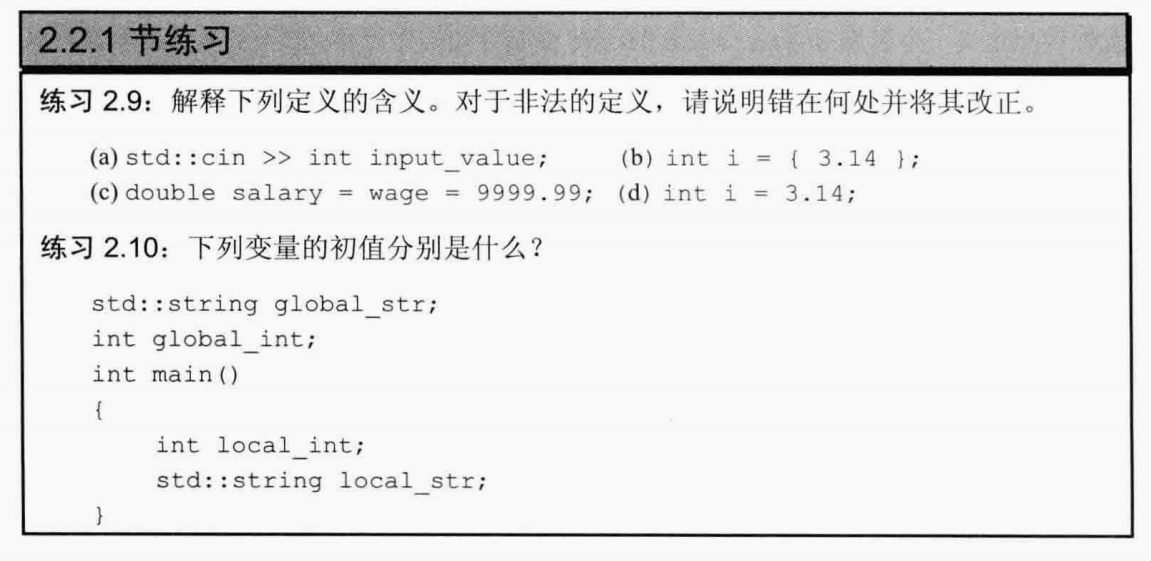
2.9:
(a)非法,>>运算符后面不能定义
(b)非法,花括号进行列表初始化可能会丢失数据,转换未执行
(c)非法,同一语句的初始化应当分别进行
(d)正确,将3.14强制转换为int型后将i初始化
2.10:
global_str = “”;
global_int = 0;
local_int 和 local_str未初始化
2.2.2
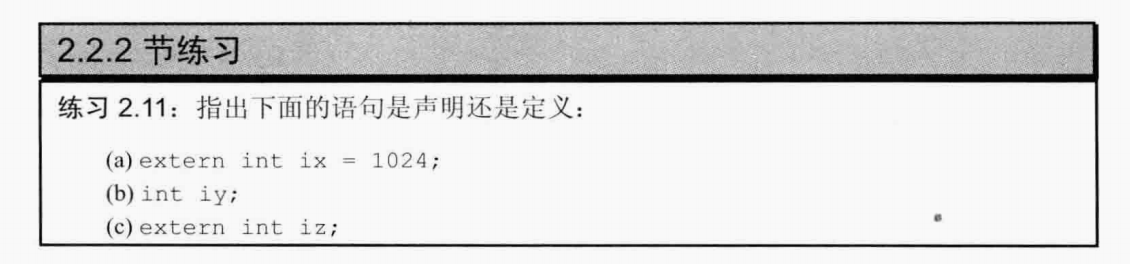
2.11:
(a)定义,因为直接将ix初始化抵消了extern的作用
(b)声明并定义,不过没有初始化
(c)声明,使用了extern关键字
2.2.3

2.12:
(a)非法,关键字
(b)合法
(c)非法,不能包含“-”号
(d)非法,只能以字幕开头
(e)合法
2.2.4

2.13:
j = 100;
2.14:
合法,100 45
2.3.1

2.15:
(a)合法
(b)不合法,引用的初始值必须是对象
(c)合法
(d)不合法,引用必须初始化
2.16:
(a)合法,将3.14159赋给d
(b)合法,将0赋值给了d
(c)合法,将0赋值给了i
(d)合法,将0赋值给了i
2.3.2

2.19:
指针是变量,具有自己的地址空间,可以更改指向的同类型对象,无需在定义时赋初值
引用不是变量,没有自己的地址空间,不可以更改引用的指向,它是变量的一个别名
2.20:
将i * i 赋值给了i
2.3.3

(a)
ip是指向int类型的未初始化指针,i是一个int类型的变量,r是对i的引用
(b)
i是int类型的变量,ip是指向int类型的空指针
(c)
ip是指向int类型的未初始化指针,ip2是int类型的变量
2.3.4

2.26:
(a)不合法,常量必须初始化
(b)合法
(c)合法
(d)不合法,试图修改buf常量的值
2.4.2
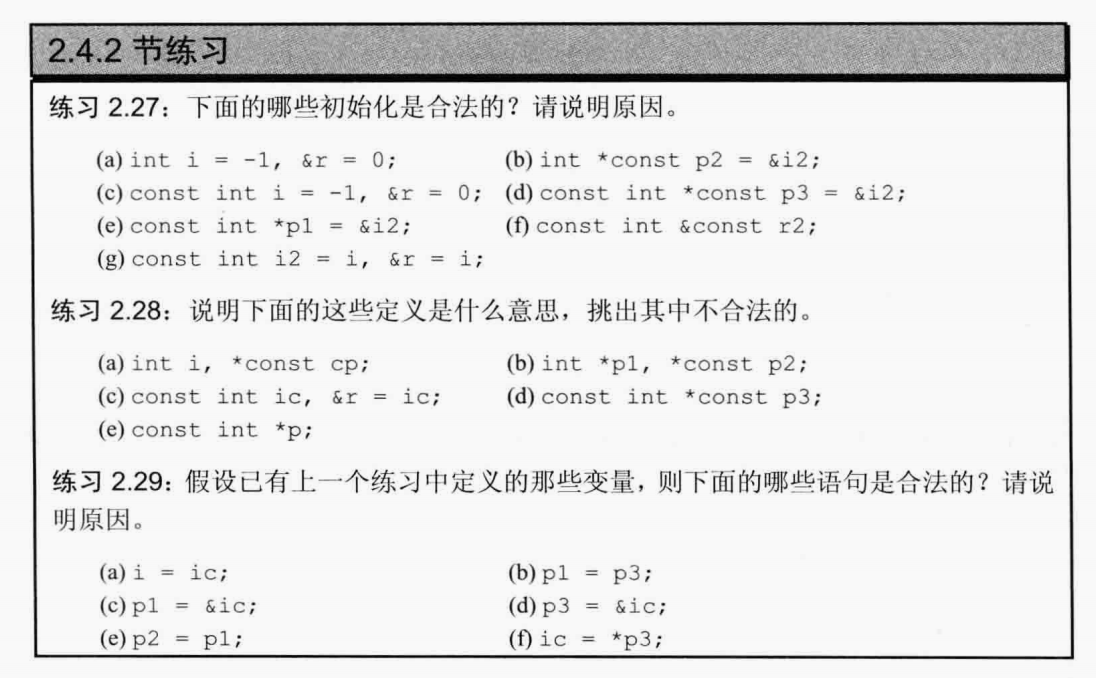
2.27:
(a)不合法,0是常量,&r不是常量应用
(b)如果i2是const int则不合法
(c)合法
(d)合法
(e)合法
(f)不合法,引用未初始化
(g)合法
2.28:
(a)不合法,cp未初始化
(b)不合法,p2未初始化
(c)不合法,ic未初始化
(d)不合法,p3未初始化
(e)合法,指针常量的指针可以不初始化
2.29:
2.4.3

2.30:
顶层
p2底层,p3既是顶层又是底层,r2底层
2.31:
合法,v2顶层是const
非法,p2底层是const
合法,p2底层const不影响
非法,p3底层是const,p1没有
合法,底层都是const
2.4.4

2.32:
非法,int null = 0, *p = &null;
2.5.2

2.33:
a = 42、b = 42、c = 42、非法、非法、非法
2.35:
j是整型,k是对整型常量的引用,p是指向整型变量的指针
j2常量int,k2常量int的引用
2.5.3

2.36:
a:int,4
b:int,4
c:int,4
d:int &,4
2.37:
a:int,3
b:int,4
c:int,3
d:int &,3
2.38:
decltype处理顶层const和引用的方式与auto不同,如果decltype使用变量作为它的表达式则返回包括const和引用在内的该变量的类型,decltype的结果类型和表达式形式密切相关。比如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
int i = 10;
const int &j = i;
/*decltype指定类型和auto不一样*/
decltype(j) a = i; //a为const int &类型,绑定到i
auto b = j; //b为int类型,值=i
/*decltype指定类型和auto一样*/
decltype(j + 0) c;
auto d = j + 0;
|
2.6.1

2.39:

2.40:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
struct Sales_data
{
string book_name;
int ISBN;
Date publish_date;
double price;
};
|
2.6.2
2.6.3
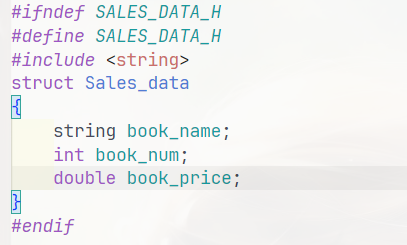
3.1

3.2.2

3.2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string str;
// getline(std::cin, str);
std::cin >> str;
std::cout << str << std::endl;
return 0;
}
|
3.3:
string类的输入运算符在遇到空格的时候就停止输入,读取到单个词,忽略了开头和结尾的空格,而getline函数会将空格读入string对象,遇到换行符停止,并将换行符丢弃
3.4:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
int main()
{
string str1, str2;
// getline(std::cin, str);
std::cin >> str1;
std::cin >> str2;
// if (str1 > str2)
// std::cout << str1;
// else
// std::cout << str2;
if (str1.size() != str2.size()){
if(str1.size() > str2.size())
std::cout << str1 << std::endl;
else
std::cout << str2 << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
3.2.3

3.6:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
string str1("Hello World!!!");
for (auto &s : str1) {
s = 'x';
}
cout << str1 << std::endl;
|
3.7:
结果一样
3.8:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
string str1("Hello World!!!");
string str2("nihao shijie");
for(string::size_type index = 0; index < str1.size(); index++)
str1[index] = 'x';
decltype(str1.size()) i = 0;
while(str2[i] != '\0') {
str2[i] = 'x';
i++;
}
|
for更好,更只管,并且声明的变量的作用域在for语句内,不会对其他程序有影响
3.3.1

3.12:
(a)正确,ivec为vector<int>类型的vector类型的对象
(b)错误,svec的类型不为vector<int>
(c)正确,svec为包含10个null字符的vector对象
3.13:
(a)0个元素 (b)10个元素,int默认初始值0
(c)10个元素,42 (d)1个元素,10
(e)两个元素,10,42 (f)10个元素,空串
(g)10个元素,“hi”
3.3.2

3.14:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
vector<int> ivec;
int temp;
while (cin >> temp)
ivec.push_back(temp);
for (decltype(ivec.size()) i = 0; i < ivec.size(); i++) {
cout << ivec[i] << endl;
}
|
3.15:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
vector<string> svec;
string temp;
while (cin >> temp)
ivec.push_back(temp);
for (decltype(svec.size()) i = 0; i < svec.size(); i++) {
cout << svec[i] << endl;
}
|
3.3.3

3.16:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::vector;
//懒得写函数了,,,凑合凑合吧
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2(10);
vector<int> v3(10, 42);
vector<int> v4{10};
vector<int> v5{10, 42};
vector<string> v6{10};
vector<string> v7{10, "hi"};
for (decltype(v1.size()) index = 0; index < v1.size(); index++) {
std::cout << v1[index] << std::endl;
}
for (decltype(v2.size()) index = 0; index < v2.size(); index++) {
std::cout << v2[index] << std::endl;
}
for (decltype(v3.size()) index = 0; index < v3.size(); index++) {
std::cout << v3[index] << std::endl;
}
for (decltype(v4.size()) index = 0; index < v4.size(); index++) {
std::cout << v4[index] << std::endl;
}
for (decltype(v5.size()) index = 0; index < v5.size(); index++) {
std::cout << v5[index] << std::endl;
}
for (decltype(v6.size()) index = 0; index < v6.size(); index++) {
std::cout << v6[index] << std::endl;
}
for (decltype(v7.size()) index = 0; index < v7.size(); index++) {
std::cout << v7[index] << std::endl;
}
}
|
3.17:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cctype>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
int main()
{
vector<string> svec;
string s;
while (std::cin >> s) {
svec.push_back(s);
}
for (auto &s : svec){
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
toupper(s[i]);
}
for (auto s : svec)
std::cout << s << std::endl;
return 0;
}
|
3.18:
不合法,ivec没有元素
可以改成:vector<int> ivec(1);有一个元素,且下标从0开始
3.4.1

3.21:
关键代码:
1
2
|
for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it)
std::cout << *it << std::endl;
|
3.22:
关键代码:
for (auto it = text.cbegin(); it = text.cend() && !it->empty(); ++it)
std::cout << *it << std::endl;
3.23:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec(10, 2);
for (auto it = ivec.cbegin(); it != ivec.cend(); ++it)
//注意解引用的时候加括号,这是这道题的考察点
std::cout << (*it) * 2 << std::endl;
return 0;
}
|
3.4.2

3.24:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec;
int i = 0;
while (std::cin >> i)
ivec.push_back(i);
auto beg = ivec.cbegin(), end = ivec.cend();
for (auto it = beg, eit = end - 1; it <= beg + (end - beg) / 2; ++it, --eit) {
std::cout << (*it) + (*eit)<< std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
3.25:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
int main()
{
vector<int> index(11, 0);
auto it = index.begin();
int score;
while (std::cin >> score) {
auto it = index.begin();
it += score / 10;
(*it)++;
}
for (auto temp = index.cbegin(); temp != index.cend(); ++temp)
std::cout << *temp << ' ';
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
|
3.26:
在数据量很大的时候可能会出现溢出,而使用减法一定不会溢出,
3.5.1

3.27:
(a)非法,buf_size不是常量表达式 (b)合法
(c)非法,txt_size()返回值不是常量类型 (d)非法,没有空字符的位置
3.28:
sa为10个空字符、ia为10个0、sa2空串、ia2不确定值
3.29:
①不够灵活:大小是固定的不可扩展
②没有API
3.5.2

3.30:
数组索引从0开始,长度为10的数组索引值为0~9,最后取不到10
3.31:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
std::cout << arr[i] << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
|
3.32:
关键代码:
1
2
3
4
5
|
int arrCopy[10] = {};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arrCopy[i] = arr[i];
std::cout << arrCopy[i] << ' ';
}
|
重写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec(10, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < ivec.size(); i++) {
ivec[i] = i;
std::cout << ivec[i] << ' ';
}
std::cout << std::endl;
vector<int> ivec1 = ivec;
for (auto a : ivec1)
std::cout << a << ' ';
return 0;
}
|
3.5.3
3.34:将p2赋值给p1,p1或p2非法则程序非法
3.35:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[10];
int *p = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
*p = 0;
p++;
}
for (int i : arr)
cout << i << endl;
return 0;
}
|
3.36:
3.5.4

3.37:无’\0’,循环可能不会停止,可能打印不确定的信息(有风险)。
3.38:两个指针相加得到一个新指针,但是指向的内存地址的内容我们不知道,也不知道有什么用
3.39:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a = "aabb";
string b = "aabb";
if (a == b)
cout << "equal" << endl;
else
cout << "not equal" << endl;
char c[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
char d[] = "abc"; //有空字符'\0'
if (strcmp(c, d) == 0)
cout << "equal" << endl;
else
cout << "not equal" << endl;
return 0;
}
|
3.5.5
3.41:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40};
vector<int> vec(begin(arr), end(arr));
for (int a : vec) {
cout << a << ' ' << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
3.42
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int main()
{
vector<int> vec(3, 2);
int arr[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
arr[i] = vec[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
cout << arr[i] << ' ' << endl;
return 0;
}
|
3.6

3.43:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
//版本1
int ia[2][3] = {{1, 1, 1}, {2, 2, 2}};
for (int (&a)[3] : ia) {
for (int b : a)
cout << b << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
//版本2
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
cout << ia[i][j] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
//版本3
for (int (*p)[3] = ia; p != ia + 2; p++) {
for (int *q = *p; q != *p + 3; q++)
cout << *q << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
|
3.34:
3.35:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
for (int_array *p = ia; p != ia + 2; p++) {
for (int *q = *p; q != *p + 3; q++)
cout << *q << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
for (auto p = begin(ia); p != end(ia); p++) {
for (auto q = begin(*p); q != end(*p); q++)
cout << *q << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
|
4.1.2

4.1:105
4.2:(a)*(vec.begin()) (b)(*vec.begin()) + 1
4.1.3

4.3:
答:我认为可以接受,我们可以人为的多注意,效率必须是C++的优势。
4.2
4.4:
(((12/3) *4) +(5*5)) + ((24%4)/2) 结果为91
4.5:
(a)-86 (b)-18 (c)0 (d)-2
4.6:
a % 2 == 0 ? "偶数" : "奇数"
4.3

4.8:都是先求左侧,如果左侧无法判断结果再求右侧
4.9:先判断cp,如果不是空指针,再判断*cp
4.10:while (cin >> i && i != 42)
4.4

4.13:
(a) i = 3,d = 3.0 (b) i = 3,d = 3.5
4.14:
第一句非法,42是右值。第二句会执行if语句内的内容
4.15:
因为不能将指针赋值给int和double,可以修改为
1
2
3
|
double dval; int ival; int *pi;
dval = ival = 0;
pi = 0;
|
4.5

4.17:前置返回将其本身加1后返回,而后置将其加一后返回初始值的副本
4.18:可能会访问不存在的元素
4.19:
(a)ptr不为空且ptr指向的值不为空,并让ptr指向下一个位置
(b)ival不为0且ival+1不为0
(c)非法,因为左右两侧都用到了ival,具有二义性,可以改成vec[ival] <= vec[ival + 1];
4.6

4.20:
(a) 合法,解引用iter并让iter指向下一个位置 (b) 非法,试图将string+1,
(c) 非法,迭代器没有empty成员 (d) 合法,iter指向的string对象的empty成员
(e) 非法,字符串不能++ (f) 合法,先判断iter指向的string对象是否为空再++
4.7

4.21:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
v.push_back(i);
for (int &x : v) {
if (x & 1) {
cout << x << endl;
x *= 2;
}
}
return 0;
}
|
4.22:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int score = 100;
string lv;
lv = (score < 60) ? "fail" : (score > 90) ? "high pass" : (score > 75) ? "pass" : "low pass";
cout << lv << endl;
return 0;
}
|
多个if语句显然更好理解,因为条件运算符包含了多重嵌套,阅读起来比较费力
4.23:
+的优先级大于==和?,所以会先执行s + s[size() - 1] ,不符合题意,并且string不能与char比较,应修改为:
1
2
|
string s = "word";
string p1 = s + (s[size() - 1] == "s" ? "" : "s");
|
4.8

4.25: 结果未定义,在对q取反的时候会转换成int类型,而取反后得到一个负数,如果一个对象是带符号的值而且为负,那么这里的移位运算符如何处理符号位依赖于机器
4.26:在不同的机器上int最小位数不一定,可能存在int占16位的情况,导致位数不够
4.27:
(a)3 (b)7
(c)true (d)true
4.9

4.28:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
int main()
{
cout << sizeof(bool) << endl;
cout << sizeof(char) << endl;
cout << sizeof(short) << endl;
cout << sizeof(int) << endl;
cout << sizeof(float) << endl;
cout << sizeof(long) << endl;
cout << sizeof(double) << endl;
cout << sizeof(long long) << endl;
cout << sizeof(long double) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
4.29:10, 2
4.30:
(a)(sizeof x) + y (b)sizeof(p->men[i])
(c)(sizeof a) < b (d)sizeof(f())
4.10

4.31:后置版本会保存未修改的值并返回,如果不需要则使用前置版本。不需要做改动
4.32:两种遍历数组的方式,iptr是指针,ix是索引
4.33:(someValue ? ++x, ++y : –x), –y
4.11.1

4.34:
4.11.3

5.1

5.2

5.3.1

5.3.2

5.4.1

5.4.2

5.4.4

5.5.1

5.5.2

5.5.3
5.6.3

6.1

6.1.1

6.1.2
6.1.3

6.2.1

6.2.2

6.2.3

6.2.4

6.2.5

6.2.6

6.3.2

6.3.3

6.4

6.5.1

6.5.2

6.5.3

6.6

6.6.1

















































































